TOP Sectors of Ukrainian Economy - AgriFood
The agricultural sector has a significant potential to stimulate economic growth in Ukraine

The Investment Guide, prepared by the KSE Institute in collaboration with the Ministry of Economy of Ukraine, is an informational publication focusing on significant investment opportunities and economic developments in Ukraine. The analysis presented aims to offer insights for investors, experts, and researchers interested in economic policies, reconstruction efforts, and investment activities in Ukraine
May 2024
Copyright © 2024 Kyiv School of Economics. All rights reserved.
The Guide presents information on the following priority sectors of Ukrainain economy:
- Agrifood
- Transportation & Logistics
- Energy
- Hydrogen
- Green steel
- Critical raw materials
- Housing, reconstruction and building materials
- Pharmaceutical and Medical sectors
- ICT and digital sector
Read about TOP sectors in the Netherlands on this link Topsectoren
AgriFood sector overview
page 31 of the Guide. Chapter 4.1
4.1.1. Current situation and the sector role in the economy of ukraine and global food security
Ukraine is one of the guarantors of food security in the world, contributing to the global food market with the capacity to feed about 400 million people.1 Before Russia’s invasion, Ukraine supplied 50% of the grain stock of the UN World Food Program, the largest humanitarian organisation in the world. The agrifood sector plays a key role in Ukraine’s economy.
The agrifood sector has shown much resilience, remaining a powerful component of the country’s exports. In 2023, the share of agri-food products in the total exports of Ukraine increased to 62% compared to 41% in 2021.
Exports
Ukraine remains a key supplier of grain and sunflower oil in the world markets. Despite its size, Ukrainian agriculture relies on exporting competitive but low-added-value grains and oilseeds. With regard to the more profitable prepared foods (excluding oilseed cake), Ukraine is a net importer, and these products represent only 6% of Ukraine’s trade with the EU.
Processed products, livestock sector, and creating added value
Almost 80% of Ukraine’s exports are raw commodities or partially processed products.
Ukraine has significant resources for biofuel production which are currently underexploited, but could potentially support European energy and climate goals as well as contribute to the development of the domestic market.
The livestock sector in Ukraine is important for ensuring the country’s food security, however, the market is characterised by a steady tendency to reduce the number of almost all types of livestock.
The war and agribusiness – key developments and issues
Prior to the Russian invasion, 98% of Ukraine’s grain exports were transported through the Black Sea11. The disruption of the grain agreement and the blockade of shipping in the Black Sea affected the structure of logistics routes. The role of land transport has increased significantly.
About 25% of Ukrainian lands have been contaminated with landmines and unexploded ordnance. Ukraine is interested in increasing the number and expanding the existing programs for demining the lands of small farmers and supporting agricultural producers initiated by international institutions.
The destroyed Kakhovka HPP aggravated the problem of water supply. Over 300,000 hectares will now depend on uncertain rain-fed irrigation, resulting in productivity losses of up to 70%. Reclamation and irrigation systems for land restoration are becoming more relevant, which has attracted the interest of international donors and investors.
Overview of key players in the sector and successful cases of recent years
Ukraine’s agricultural sector is characterised by a competitive market environment. Market players vary in size: large domestic companies and subsidiaries of international groups operate alongside small local farmers. SMEs are responsible for over 83% of product sales, while the share of large enterprises is lower at 16%.
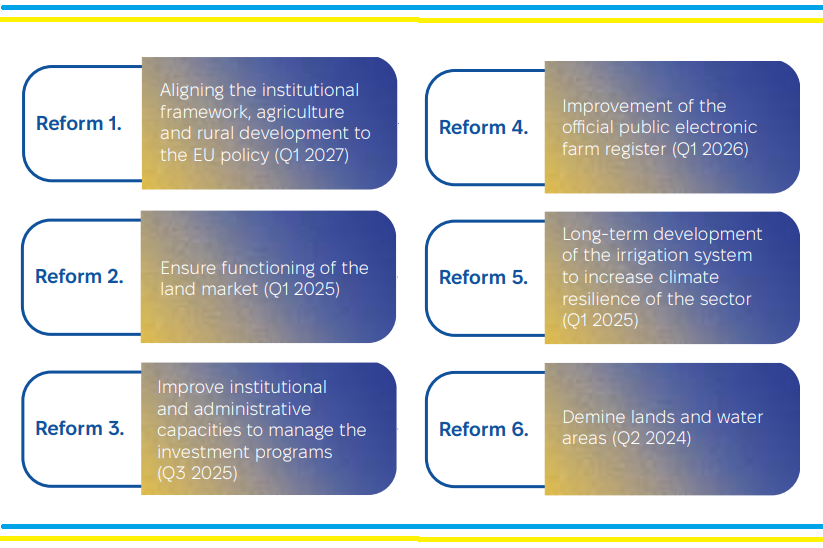
4.1.2. Overview and outlook of key reforms
The list of reforms is not exhaustive. The Ukrainian government is also working to strengthen export logistics by opening new international checkpoints, speeding up cargo inspection procedures and expanding border capacity. Ukraine is actively allocating funds to restore critical logistics infrastructure (including rail and road networks) through the Restoration of Critical Logistics Infrastructure and Network Connectivity project
4.1.3. Tendencies and trends
- Climate Change and Resource Sustainability
- Digitalization and Automation
- Bioeconomy and Circular Economy
- Global Food Demand Increase
- Changes in Global Trade and Policy
- Enhanced Quality and Safety Standards
- Expansion of Markets for Organic Produce
4.1.4. Prospects and potential for the sector
Seeds – substituting imports
Fertilisers – substituting imports and introducing green technologies
Plant protection products (ppps) – localising the production by international players
Agricultural equipment – localising the manufacture of heavy self-propelled machinery, developing attachment equipment and accessories and innovative technologies
Irrigation – increasing irrigation capacities
Development of food processing industry
Livestock sector – developing infrastructure to increase exports
Highlighted investment projects
Ukraine Investment Guide was presented at the Ukraine Recovery Conference 2024 in Berlin.
The Guide offers a comprehensive overview of Ukraine's economic policy and investment opportunities, detailing 95 projects requiring approximately $27 billion in financing. This guide is the result of collaborative efforts with KPMG, EY, Deloitte, BDO, and the Tony Blair Institute.
The Guide and the assembled investment projects are the results of work in sectoral groups with businesses, organized with the information and analytical support of the Kyiv School of Economics. Since July 2023, more than 1,100 projects have been assembled, with varying degrees of readiness and level of elaboration.
With global trends like decarbonization and energy needs, Ukraine is ripe for opportunity. The Government supports investors with guarantees, war risk insurance, and state programs. New co-financing mechanisms with IFIs and DFIs will further support private investment.
Key highlights of the Investment Guide include:
🔹Investment Projects: The guide outlines 95 projects in priority sectors such as energy, infrastructure, agri-food, green steel, pharmaceuticals, critical materials, and IT.
🔹Strategic Opportunities: Investing in Ukraine now provides strategic advantages with significant returns in the medium to long term.
🔹Sectoral Development: Emphasis on developing priority sectors and the processing industry to resolve export logistics issues and enhance high-value-added industries.
🔹Market Potential: With global trends like decarbonization and significant energy needs, Ukraine offers ample investment opportunities.
Explore the full Ukraine Investment Guide and discover investment opportunities here: https://t.ly/8M7r6